What Is Counter IC? The Complete Guide
What is Counter IC? The Complete Guide
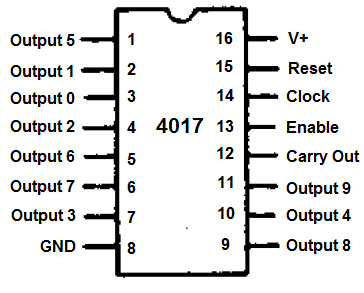
Image source Rantle East Electronic
Let’s say you are building an electronic device and one of its functions entails counting objects. Among the many components that you should integrate into your solution is a counter IC.
A counter IC is a semiconductor chip that is capable of counting objects. It can count to ten and beyond.
This chip has counter increments that align with each rising clock pulse. In doing so, they can increment the numerical value of each specific event or object.
The data from the counter IC can be used to trigger an action on the other end of an application or circuit.
Are you planning to buy a counter IC for your electronic application? This is a perfect guide for you. We are going to break down everything that you should know about these chips.
How counter ICs work
A typical counter IC has a sequential logic circuit whose input terminals accept the input signals while the output terminal produces the count values in integers.
At each clock edge, the circuit will perform either an increment or decrement depending on the design of the circuit.
The counting mechanism is activated once the circuit has been switched on. Some counters have a reset button that allows users to erase the previous count and start afresh. In some cases, the count starts from the previous value.
This implies that a counter IC has memory capacity that stores data on all the counts. Usually, the state of the count is known once you initialize the chip.
As the chip is in an ON state, counting will commence when it receives a clock signal. This will serve as the input signal to the counter. The input signals are usually from various external sources. They are the key determinants of each count's increment and decrement values.
Once the clock input signals have been fed into the counter IC, the next phase is the counting sequence.
Internally, counter ICs utilize flip-flop circuits to record the current counts while at the same time retaining counts that are between the clocks.
The output from the count may be a direct representation of the counts. This is usually represented in binary numbers. Sometimes the output is encoded to produce gray codes.
The operation of counter IC tends to follow a particular sequence as follows:
· Reset: This step entails setting the counter to zero. In some counters, this is referred to as clear or master reset. It is usually done before a new counting session.
· Enable: This step allows the counting session to commence
· Direction: Here, the counter IC determines whether the count will be increment or decrement
· Data: This is the information about the current count. It gives the count value.
Some counter ICs have terminal count output. This is designed to indicate the next clock that will trigger the outflow of the count value. This feature is commonly used when two counter ICs are used in a single major counter device. To create this, the terminal count output of one counter is connected to the Enable input of another counter.
Operation of a counter IC
Since these are semiconductor chips, they comprise passive electronic components that are connected to form electronic circuits.
Each component in the circuit has a specific role to play, especially the counting role.
The most important components that make it possible for the device to count are the logic gates. They are responsible for executing logic operations in electric devices.
All the major logic gates are used to form a device. These are AND, OR, NOT, and NAND, among others. The result of this connection is a complex circuit that can execute different roles, such as counting objects.
The output data from the logic gates is stored in the flip-flops. These are designed to store binary data (0s and 1s) that is coming from the gate. The flip-flops store the values of the counts.
The counting operation is controlled by the clock signal. It takes note of the count values, increments, and even decrements. The clock signals are measured in pulses. Each pulse triggers the chip to update the state of the count value.
Processing and output
Now that you have the values from the counting process, the next step is to process the data for further action.
Decoders are used for this role. They interpret the count values and then pass them to the next level.
In most cases, count values are used for triggering different actions depending on the application area of the counter.
For example, the count may trigger an alarm.
A display module may be connected to the circuit to display the count.
Types of counter ICs
Different types of counter ICs are used for different purposes and in different application areas.
The most common types include asynchronous counter IC, synchronous counter, modulus counter Ic, decade counter, ring counter, and gray-code counter.
Let’s look at the differences between these counter ICs and you will be in a position to tell which chip is suitable for you.
Asynchronous counter IC
In the asynchronous counter, the state of each flip-flop is determined by the state of the previous flip-flop.
This chip is also known as the ripple counter or toggle counter as it records the state of each flip-flop in the circuit.
The counter values of all the other flip-flops are determined by the output of the nearest flip-flop that has a minimal significant value. While doing so, each flip-flop introduces a delay of the clock signal to the output signal. This ends up changing the counterbits, which results in ripple effects.
Given the serial operation of the asynchronous counters, they are quite limited in terms of speed. This problem is solved by applying clock pulses on each flip-flop at the same time. This ends up balancing the settling time of the flip-flops and the propagation time. However, this modification means that more hardware has to be introduced to the circuit.
Synchronous counter IC
This name is derived from the management of the flip-flops. Here, the input signals of the flip-flops are connected to a clock. The result is all the flip-flops are triggered simultaneously. All of them change their states at the same time.
In synchronous counter ICs, the output signal of one flip-flop is not directly connected to the input signal of the next signal.
The working mechanism of synchronous IC eliminates the problem of propagation delay, which is synonymous with asynchronous IC. They also have a speed advantage over the asynchronous ICs.
Decade counter IC
A decade counter IC is designed to count in decimal numbers instead of binary numbers like other chips. It can count up to a binary of 1001 which is 9 in decimal numbers.
This counter is designed by adding a NANF gate to the four-stage counter chip.
The working mechanism of a decade counter is slightly similar to that of an asynchronous counter IC. Each input pulse has an increment of one until it reaches the maximum which is nine. Once the pulse reaches 9. The extra 0 or low is considered a “carry out” and is used for triggering the next cycle of counting.
Modulus counter IC
This type of integrated circuit is designed to count through a defined number of states.
They are classified into two main categories: Mod n and Mod?n where “n” stands for the number of states.
They are ideal in applications where you would like the chip to count the number of events or even sessions.
Ring counter IC
As the name suggests, this IC is used in circular shift registers. The counting process is triggered only when one of the flip-flops is in a high state while the other flip-flops are low.
This counter IC is usually referred to as a shift register since the output of the last flip-flop is connected to the input of the next.
So, which type of counter IC should I choose? Well, it all depends on the device or application that you are building.
Conclusion
This article has provided all the vital information that you need to know about counter-integrated circuits.
Whether you are a new player in the game of electronics or you are experienced in this field, you should be able to utilize this information to your benefit.
Take that step of buying the right counter IC for your electric and electronics project.
But the biggest question is, where can I find the best counter IC? This is a question that most buyers tend to ask, especially those who intend to buy counter ICs in bulk.
The surest place is from reputable counter-IC suppliers in China. Other than stocking adequate chips, they also have the full capacity to supply high-quality semiconductor chips.
ICRFQ is one such supplier. We are a reputable global distributor of counter ICs in China. We also supply other types of semiconductor chips and counter ICs are among our products.
All you need is to contact us and we will deliver to your location. Furthermore, we accept custom orders for the counter ICs.
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With


