What is a Lithium-ion Battery? A Comprehensive Overview
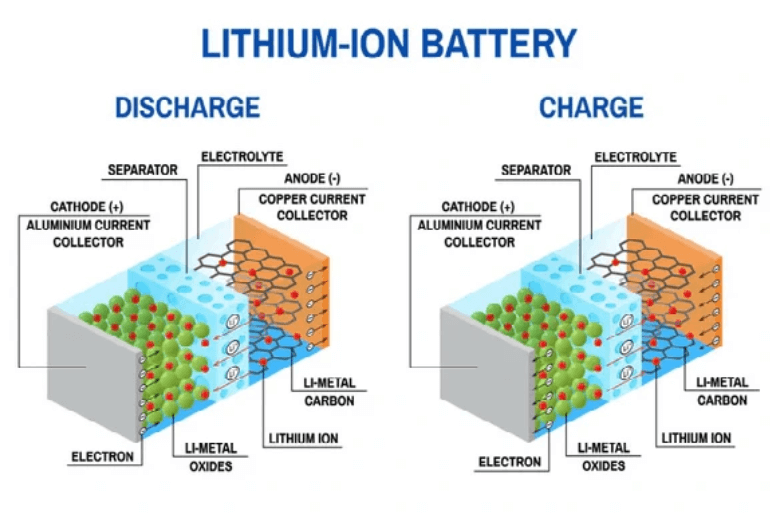
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are rechargeable energy storage devices pivotal to modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles (EVs). First commercialized by Sony in 1991, they revolutionized portable electronics and continue to drive advancements in renewable energy and transportation.
2. Components and Structure
A Li-ion battery comprises four key components:
Cathode: Typically lithium metal oxides (e.g., LiCoO?, LiFePO?).
Anode: Usually graphite, facilitating lithium-ion intercalation.
Electrolyte: A lithium salt in a solvent, enabling ion transport.
Separator: A porous polymer membrane preventing electrode contact.
Additional elements include aluminum (cathode) and copper (anode) current collectors.
3. Working Principle
Li-ion batteries operate via lithium-ion movement between electrodes during charge/discharge:
Charging: Li? ions migrate from cathode to anode; electrons flow externally.
Discharging: Li? ions return to the cathode, releasing energy.
Redox reactions occur at each electrode, with the electrolyte facilitating ion transport while insulating electrons.
4. Types of Li-Ion Batteries
Different chemistries cater to varied applications:
| Type | Chemistry | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide | LiCoO? | High energy density, limited lifespan | Smartphones, laptops |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate | LiFePO? | Thermal stability, long cycle life | EVs, power tools |
| NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) | LiNiMnCoO? | Balanced energy density/safety | EVs, grid storage |
| NCA (Nickel Cobalt Aluminum) | LiNiCoAlO? | High energy, moderate safety | Tesla vehicles |
| Lithium Titanate | Li?Ti?O?? | Ultra-fast charging, durability | Grid storage, buses |
5. Advantages
High Energy Density: Stores more energy per weight than alternatives (e.g., NiCd).
Long Cycle Life: 500–1,000+ charge cycles.
Low Self-Discharge: ~1–2% monthly, ideal for intermittent use.
No Memory Effect: Partial charging without capacity loss.
6. Disadvantages
Safety Risks: Thermal runaway from overheating or damage (e.g., Samsung Note 7 recalls).
Degradation: Capacity loss over time, accelerated by high temperatures.
Cost: Expensive raw materials (e.g., cobalt).
Environmental Impact: Mining (lithium, cobalt) and recycling challenges.
7. Applications
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, cameras.
Transportation: EVs (Tesla, Nissan Leaf), e-bikes.
Energy Storage: Grid solutions (Tesla Powerwall), renewable integration.
Medical Devices: Portable equipment, implantables.
8. Current Research and Innovations
Solid-State Batteries: Replace liquid electrolytes with solids for safety and energy gains.
Silicon Anodes: Higher capacity than graphite, though volume expansion issues persist.
Recycling Advances: Hydrometallurgical methods to recover lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
Cobalt Reduction: Developing low-cobalt cathodes (e.g., NMC 811) to cut costs and ethical concerns.
9. Challenges
Resource Scarcity: Geopolitical and ethical issues around cobalt/lithium mining.
Recycling Infrastructure: Limited economically viable methods; <5% recycled globally.
Safety Standards: Need for robust battery management systems (BMS) to prevent failures.
10. Future Prospects
Solid-State Commercialization: Companies like Toyota aim for 2025–2030 deployment.
Fast-Charging Tech: Reducing EV charging times to under 15 minutes.
Sustainability Focus: Circular economy models and second-life applications (e.g., repurposing EV batteries for grid storage).
Conclusion
Li-ion batteries are indispensable to the clean energy transition, offering unmatched energy density and versatility. While challenges like safety, cost, and sustainability persist, ongoing innovations promise to enhance their efficacy and environmental footprint, securing their role in future technologies.
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With


